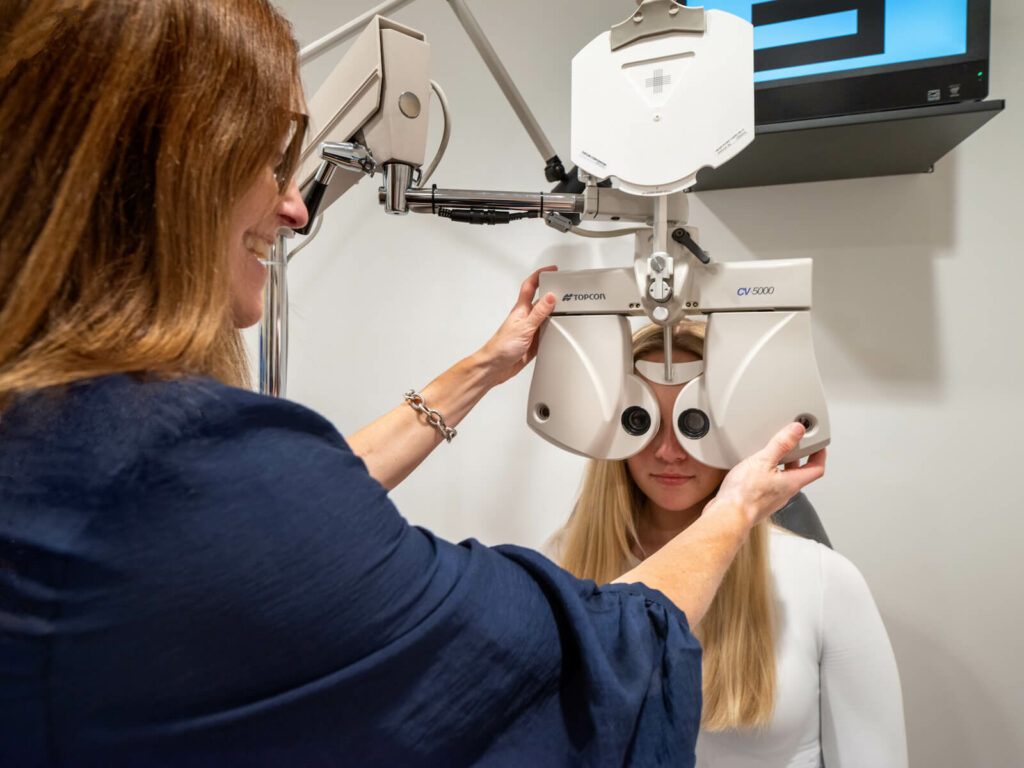
You might consider an eye exam just another check-up to make sure you have the right prescription for your glasses or contacts. However, a comprehensive eye exam can reveal more than vision issues.
Eye exams help maintain good eyesight and eye health by detecting eye diseases such as:
- Cataracts
- Glaucoma
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Diabetic eye diseases
Many eye diseases can go undiagnosed until they reach advanced stages, posing significant risks to vision and overall health. For that reason, you should have regular eye exams, even if you do not wear corrective eyewear.
What Is an Eye Exam?
An eye exam is a comprehensive evaluation of vision and overall eye health. It involves a series of tests and assessments to check for vision conditions, common eye diseases, and risk factors that may affect your eyesight.
The frequency and type of eye exams can vary depending on age and individual risk factors. Children’s eye exams focus on detecting refractive errors (nearsightedness and farsightedness), and eye muscle function, while adult and senior eye exams also look for signs of age-related changes that increase the risk for various eye diseases.
Additionally, systemic conditions such as diabetes can present in the eye, making regular diabetic eye exams crucial for early detection and management. Overall, an eye exam is an essential step in maintaining good vision and overall health.
Common Eye Diseases Detected in an Eye Exam
Many eye diseases do not present with noticeable changes to your vision in the early stages. Eye exams, at regular intervals determined by your eye doctor, help detect these eye diseases before they progress.
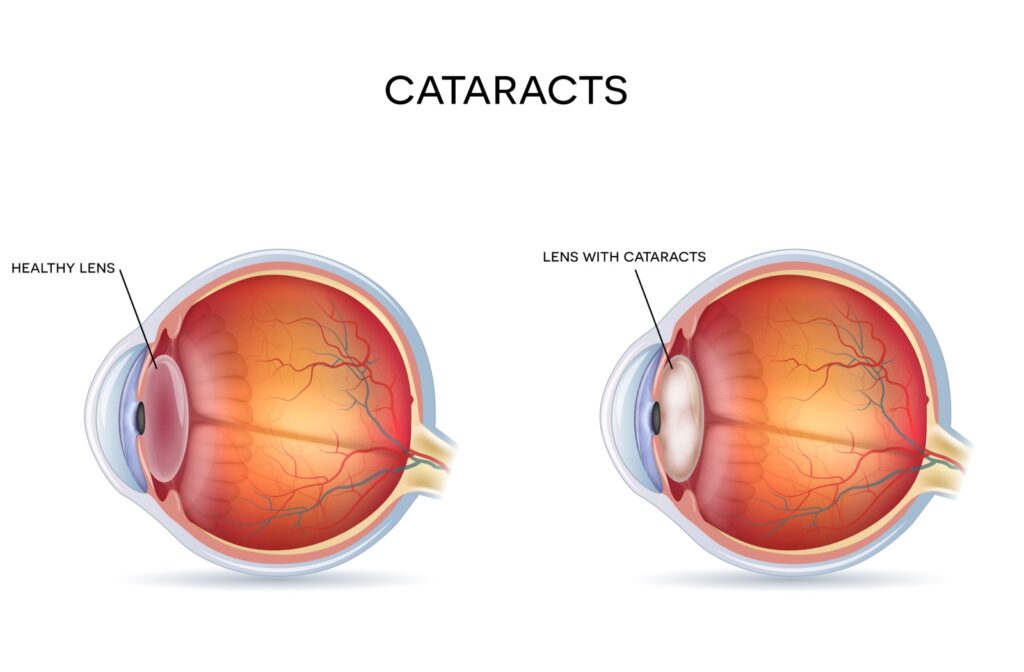
Cataracts
Cataracts are a common eye condition that can easily be detected during an eye exam. Cataracts occur when the naturally clear eye lens becomes cloudy, leading to blurred vision.
Cataracts develop slowly during the natural aging process but can also progress rapidly from injury or other medical conditions. Signs and symptoms of cataracts include cloudy or blurry vision, glare, and sensitivity to light and sometimes even colour vision changes.
During an eye exam, your eye doctor can detect early signs of cataracts with diagnostic tests and tools. Early detection is vital, as cataracts can often be managed with glasses or contact lenses initially and after surgery, restoring clearer vision.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma occurs when increased pressure within the eye damages the optic nerve at the back of the eye and can lead to irreversible vision loss. The tricky part about glaucoma, also known as the silent thief of sight, is that it often presents no symptoms until significant damage has already occurred.
During an eye exam, your eye doctor can test for glaucoma by measuring intraocular pressure using a device called a tonometer. They will assess your peripheral vision. They will also examine the optic nerve for signs of damage. Early detection is crucial for preventing vision loss, as treatments such as medications, laser therapy, or surgery can help prevent or slow down changes. Glaucoma damage can not be reversed.
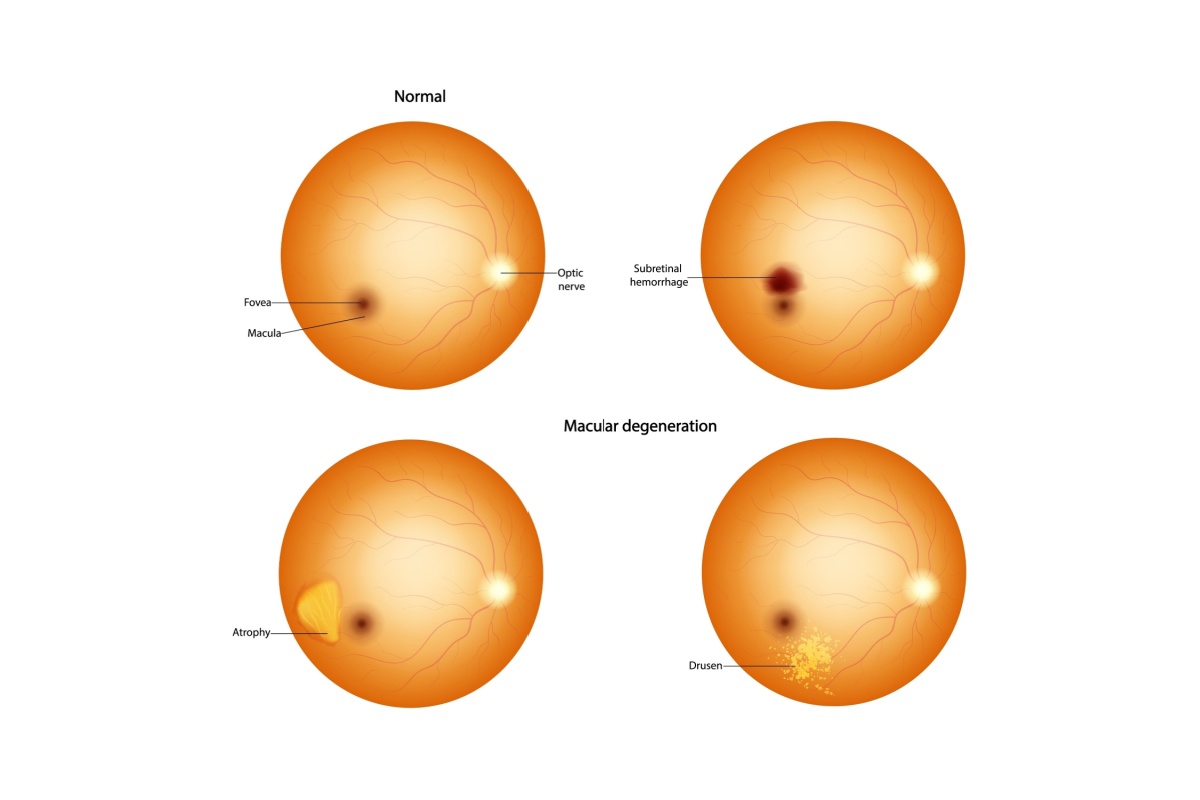
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a condition that affects the macula, the central part of the retina (the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye) responsible for sharp vision. AMD comes in two forms—wet and dry. Dry AMD is more common and progresses slowly. Wet AMD is less common but can cause rapid vision loss.
During an eye exam, your eye doctor can detect AMD with optical coherence tomography and fundus photography that allows them to look directly at the back of the eye for signs of AMD. Early detection through regular eye exams is essential for managing the condition and preserving vision.
Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetes or high blood sugar can cause damage to the tiny blood vessels in the retina, resulting in diabetic retinopathy. It can cause the blood vessels to swell, break, or leak fluid into the retina. If left untreated, it can lead to vision loss.
Diabetic retinopathy often presents no symptoms in its early stages, making regular eye exams crucial for diabetic patients. During a diabetic eye exam, your eye doctor can detect signs of diabetic retinopathy by examining cross-sectional and digital images of the retina for abnormal blood vessels or hemorrhages.
The Eye Exam Process
Understanding what happens during an eye exam can help demystify the process and highlight its importance. A comprehensive eye exam typically includes the following:
- Patient history
- Visual acuity test
- Refraction assessment
- Binocular vision
- Pupil response test
- Retinal examination
- Intraocular pressure measurement
- Front of the eye health assessment
- Visual field assessment
Eye Exams for Disease Detection & Management
Regular eye exams are essential for early detection and prevention of eye diseases. By the time symptoms become apparent in many eye conditions, significant damage may have already occurred.Don’t wait for symptoms to appear—request an appointment for an eye exam with Downtown Vision Care today and take proactive steps to protect and manage your vision and overall health.